1. Lithium Metal Batteries
Made with manganese dioxide as the positive electrode material, metallic lithium or its alloy as the negative electrode material, and non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
Features: High energy density (theoretical value up to 3,860 Wh/kg), but unstable and non-rechargeable, so they cannot be used as reusable power batteries.
2. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Made with lithium alloy metal oxide as the positive electrode material, graphite as the negative electrode material, and non-aqueous electrolyte.
Features: Equipped with rechargeable capability, making them the mainstream development direction of current power batteries; however, since positive electrode materials need to be combined with different eWements, there are significant differences in performance among various types of positive electrode materials, which in turn triggers disputes in the industry over positive electrode material technology routes.
II. Classified by Application: Two Main Application Types
1. Digital Lithium Batteries
Suitable for daily digital devices such as mobile phones, tablets, and power banks, meeting the regular power supply needs of these devices.
2. Power Lithium Batteries
Also known as “high-rate batteries”, they are mainly used in products that require high instantaneous current, including new energy vehicles of brands like Tesla and BYD, as well as drones.
Advantages: Capable of withstanding high instantaneous current, with higher technical requirements, so their price is higher than that of digital lithium batteries.
III. Classified by Shell Material: Three Common Forms
1. Steel-Cased Batteries
The shell is made of steel, with strong structural stability.
2. Aluminum-Cased Batteries
The shell is made of aluminum, which has advantages in terms of lightweight.
3. Polymer Lithium Batteries
The shell is made of polymer material, most of which are silver-colored; a small number of manufacturers produce products with black shells, commonly known as “black-shell batteries” in the industry.
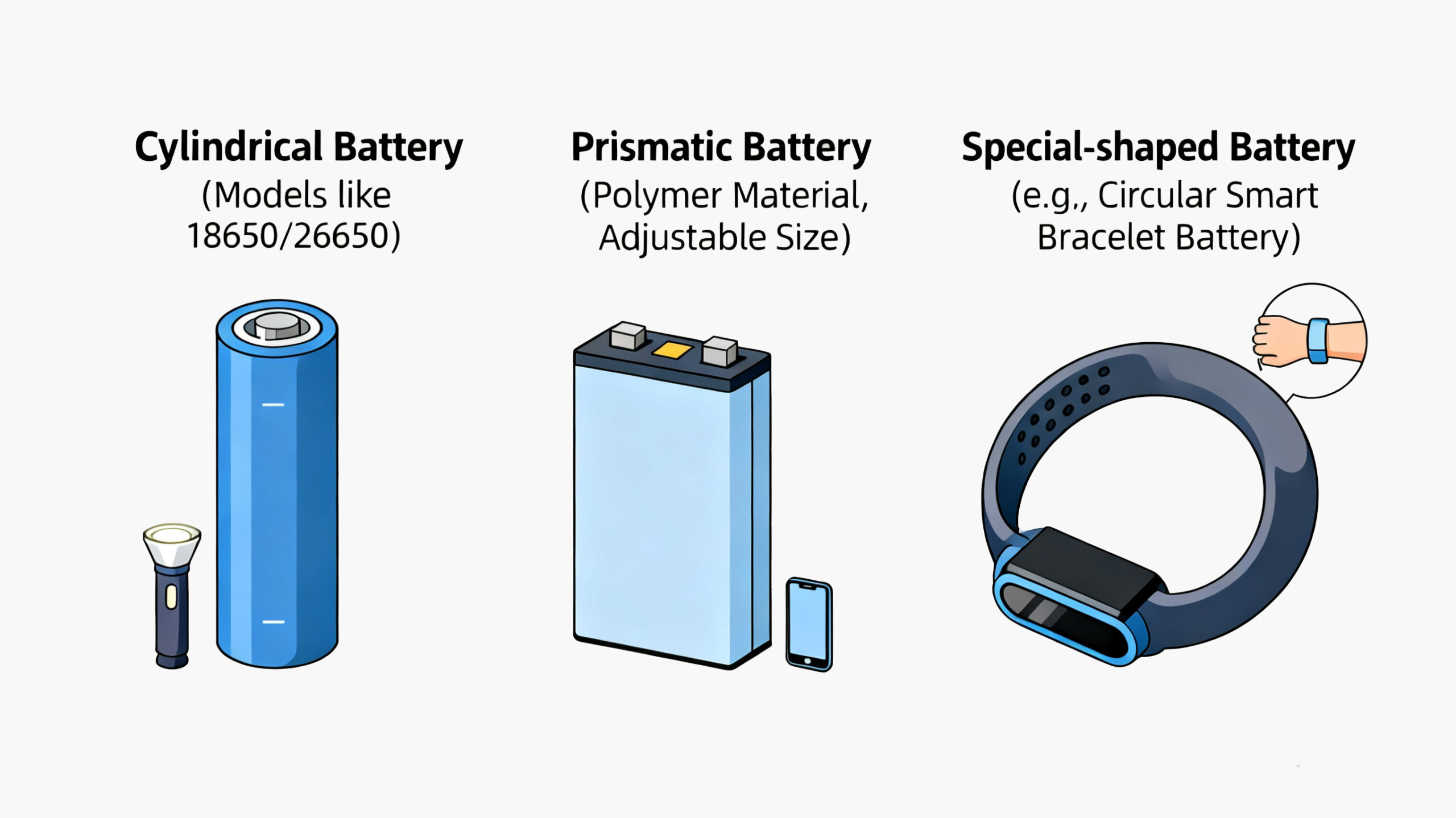
IV. Classified by Shape: Three Typical Structures
1. Cylindrical Batteries
Widely used, with common models such as 18650 and 26650, usually used in combination:
- Small combinations: Used in early laptops (requiring 8 18650 batteries) and power banks (1-6 batteries);
- Large combinations: For example, Tesla models use more than 7,000 18650 batteries for power supply through series-parallel combination.
2. Prismatic Batteries
Most are polymer lithium batteries. Due to the good ductility of polymer materials, their length, width, and height can be flexibly adjusted, which can meet the shape requirements of most digital products, making them the preferred battery type for current mainstream digital devices.
3. Special-Shaped Batteries
Irregularly shaped batteries customized according to products, which need to be accurately matched with the product structure. For example, in the currently popular smart wearable devices, circular smart bracelets are matched with corresponding circular special-shaped batteries.